About Research
Due to the uniqueness of service systems, it is often necessary to harness domain specific knowledge to improve the efficiency of algorithms and elicit insights that can be translated into effective operational policies. We will focus on healthcare service systems.
An efficient, affordable, and high-quality healthcare system is always a focus of the Singapore Government.
Due to the aging population, the growing demand for healthcare services in Singapore has severely impacted the healthcare system in recent years. It has resulted in degradation of service such as patients experiencing unbearable waiting times and severe shortages of beds in some public hospitals.
Among other measures, the Singapore Government tackles the current crunch in public hospitals by building more hospitals and increasing the bed capacity. However, apart from increasing the capacity, there are opportunities for using advance analytics for alleviating and improving healthcare service systems.
The healthcare service system is a complex interconnected system that is plagued by risk and uncertainty and that it involves multiple agents (patients, doctors, administrators) whose incentives may not necessarily be aligned.
Understandably, it is paramount to understand and unravel the complexity before meaning improvement can be made to understand the healthcare systems. Specific topics in healthcare service delivery include:
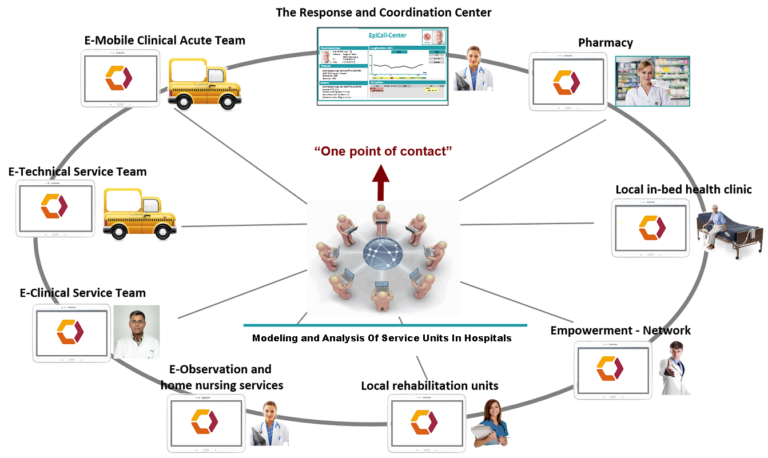
Modeling and analysis of service units in hospitals
In the hospital enviroment where there are multiple patients scenario, some patient may experience clinical deterioration during his/her stay, which can lead to serious adverse occurrences. Quick appropriate treatments and prompt detection and appropriate treatment of clinical deterioration of ward patients are essential for successful medical treatment.
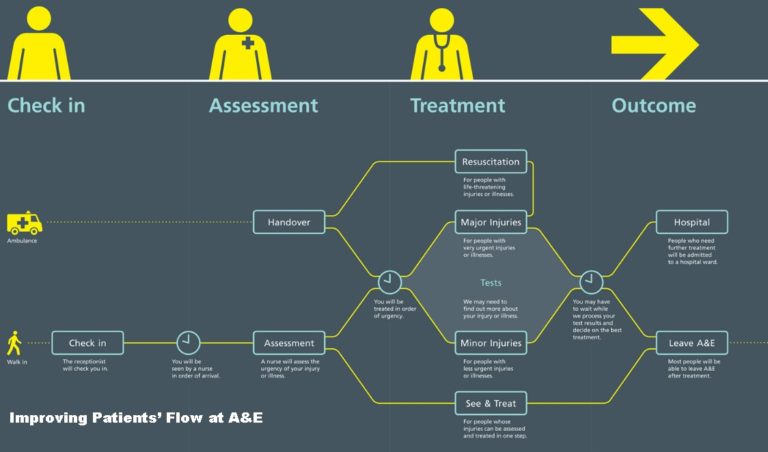
Improving patients' flow at A&E
Using analytical method based on continuous time to model and analyze the ward patient rescue process on the hospital floor. By using this method, the steady-state probabilities of various system states, such as patient in risky or non-risky conditions, nurse, physician and rapid response team interventions, or transferring to intensive care units can be evaluated to improve the transitions and correlation among different states
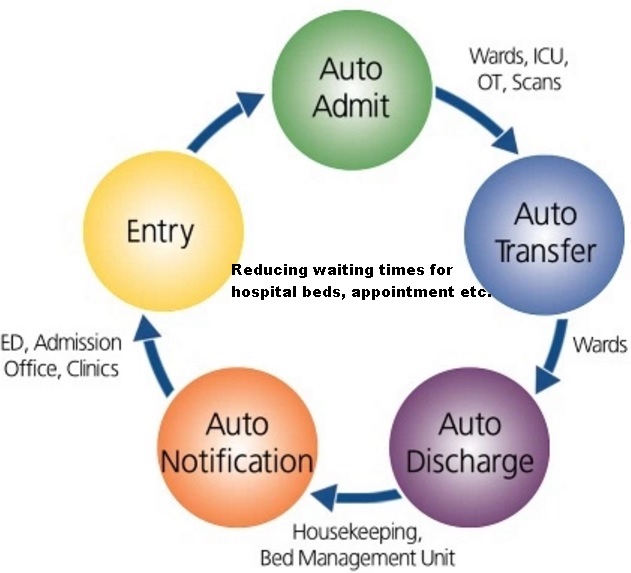
Reducing waiting times for hospitals beds, appointment
Public hospitals have always experienced a severe shortage of beds which has prolonged the waiting time for a bed. Such a bed crunch would also affect those seeking treatment at Accident and Emergency (A&E) departments, as a longer wait would be expected given that A&E medical teams would be looking into housing those waiting for a bed.
For medical appointment , a shorter wait would allow patients to have more rest at home after seeing a doctor and reduce medical complications from a prolonged stay in the waiting area with other patients.The impact here is on building is a medium- and long-term strategy to shorten waiting times through process engineering and deploying new technologies, with impact on reducing current overloading and waiting times.
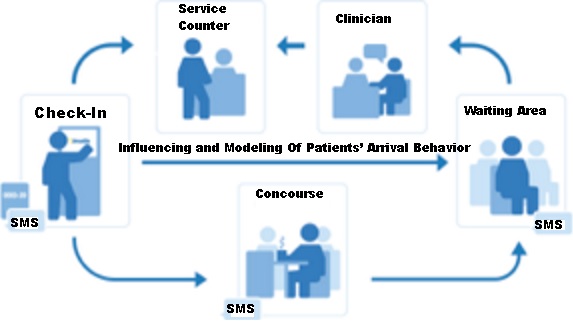
Influencing and modeling of patients’ arrival behavior
There are patients who can’t skip the wait but they can skip the waiting room. Therefore many patient travel around to avoid hanging out in the foyer of the doctor’s office all day while waiting for appointment .
To reduce wait time uncertainty and provide freedom for patients to travel around, leverage on influencing and modeling technologies to automatically reduce the anxiety and burden on patients and their caregivers currently caused by long waiting room time uncertainty.
Examples of influencing by giving patients real-time SMS updates when the doctor is running behind schedule manage patient’s expectations, it keeps them coming in. No-shows cost a significant amount of time and money they can’t get back, and text messages are drastically reducing that no-show rate.
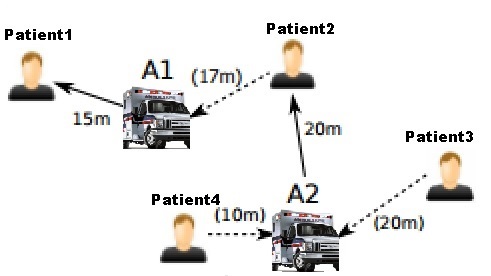
Dynamic allocations of ambulances
The life and death nature of the events involved and the generally limited availability of resources. Therefore one important resource allocation challenge is how to allocate and dynamically reposition ambulances to best serve a given set of requests.
In approach to ambulance fleet dynamic allocation and dynamic redeployment, where the goal is to position an entire fleet of ambulances to base locations to maximize the service level of the Emergency Medical Services . The take on analytics for alleviating and improving the utility of an allocation is measured by directly simulating emergency requests. This independence between request arrival patterns and behavior will be important when developing an optimization approach and analysis.